Napoleon I, French Napoléon Bonaparte, original Italian Napoleone Buonaparte, byname the Corsican or the Little Corporal, French byname Le Corse or Le Petit Caporal, (born August 15, 1769, Ajaccio, Corsica—died May 5, 1821, St. Helena Island), French general, first consul (1799–1804), and emperor of the French (1804–1814/15), one of the most celebrated personages in the history of the West.
He revolutionized military organization and training; sponsored the Napoleonic Code, the prototype of later civil-law codes; reorganized education; and established the long-lived Concordat with the papacy. (Britannica)
After seizing political power in France in a 1799 coup d’état, he crowned himself emperor in 1804. Shrewd, ambitious and a skilled military strategist, Napoleon successfully waged war against various coalitions of European nations and expanded his empire.
After a streak of victories, France secured a dominant position in continental Europe and Napoleon maintained the French sphere of influence through the formation of extensive alliances.
However, after a disastrous French invasion of Russia in 1812, Napoleon abdicated the throne two years later and was exiled to the island of Elba.
In 1815, he briefly returned to power in his Hundred Days campaign. After a crushing defeat at the Battle of Waterloo, he abdicated once again and was exiled to the remote island of Saint Helena. (History-com)
Napoleon Bonaparte died (apparently of stomach cancer) at 5:49pm on May 5, 1821, at Longwood on the island of Saint Helena.
Napoleon’s rise and prominence in power was concurrent with George Washington, and … Kamehameha.
George Washington (February 22, 1732 – December 14, 1799)
The first president of the United States, George Washington, serving from 1789 to 1797, is often referred to as the Father of Our Country.
He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783.
After victory had been finalized in 1783, Washington resigned rather than seize power, proving his opposition to dictatorship and his commitment to the emerging American political ideology of republicanism. Washington was elected as the first president in 1789, and re-elected 1792.
Dissatisfied with the weaknesses of Articles of Confederation, in 1787, Washington presided over the Constitutional Convention that drafted the United States Constitution.
Kamehameha I (ca. 1758 – May 8, 1819)
Kamehameha was initially known as Paiʻea, which means “hard-shelled crab;” Kamehameha means “The Lonely One.” Raised in the royal court of his uncle, Kalaniʻōpuʻu, Kamehameha achieved prominence in 1782, upon Kalaniʻōpuʻu’s death.
While the kingship was inherited by Kalaniʻōpuʻu’s son Kiwalaʻo, Kamehameha was given the prominent position of guardianship of the Hawaiian god of war, Kūkaʻilimoku.
In 1785, Kamehameha married Ka‘ahumanu, the daughter of one of his most trusted advisors. In 1790, he attained control of Hawai‘i Island, then he successfully invaded the Islands of Maui, Lāna‘i, Molokai and O‘ahu, by 1795.
Ultimately, in 1810, Kauai’s Kaumuali‘i decided to peacefully yield and unite with Kamehameha and join the rest of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi.
Kamehameha instituted the Kānāwai Māmalahoe, the Law of the Splintered Paddle. The law, “Let every elderly person, woman and child lie by the roadside in safety,” is enshrined in the state constitution, Article 9, Section 10, and has become a model for modern human rights law regarding the treatment of civilians and other non-combatants.
In the Islands …
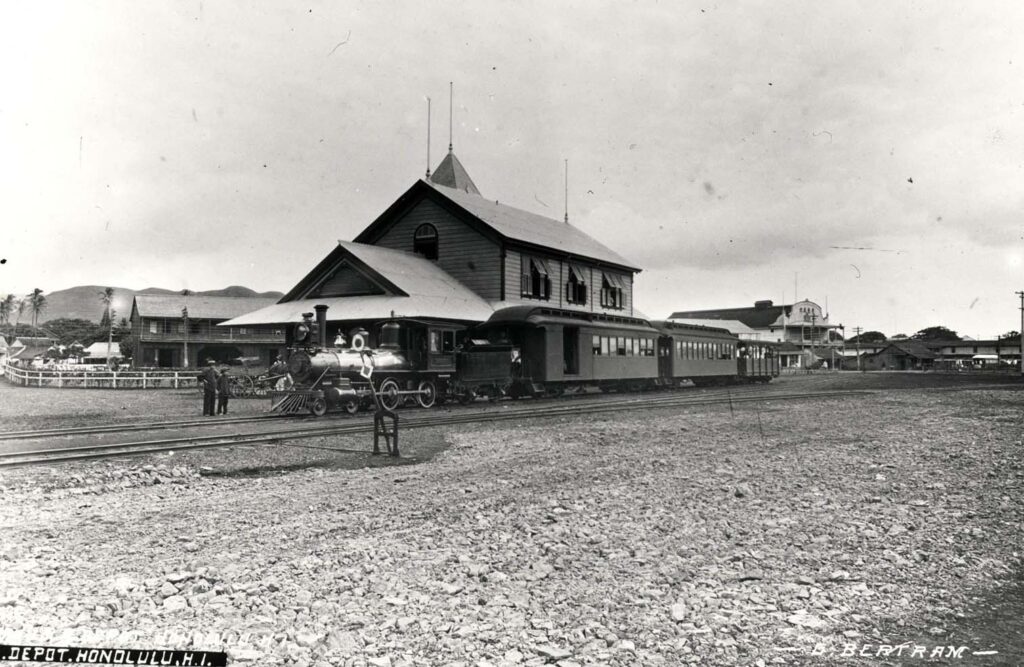
1821 Wood Frame House
The wood-framed Mission House, built in 1821, was one of the first wood-framed buildings built in Hawai‘i. The frame house stands on the grounds of the Hawaiian Mission Houses, near Kawaiahaʻo Church on the makai side of King Street.
It is the oldest wood frame structure and the oldest intact Western structure still standing in the Hawaiian Islands.
The timbers of Maine white pine were cut and fitted in Boston in 1819 and came around the Horn on the brig Thaddeus with the first mission company in April 1820, arriving first in Kona. The frame of the house arrived in Honolulu on Christmas morning of that year on board the ship Tartar.
Since the lumber for this New England plan type was actually pre-cut prior to shipment, it could also be considered in a broad sense a very early example of prefabrication.
Architecturally, it has a simple and straight-forward design; the relatively low ceilings, and basement are strong evidence of its New England concept, foreign to the temperate climate of Honolulu.
The Frame House was used as a communal home by many missionary families who shared it with island visitors and boarders. It served as a residence for various missionaries, including Hiram Bingham, Gerrit Parmele Judd and Elisha Loomis.
Today the frame house is maintained by the Hawaiian Mission Children’s Society as a memorial to the early missionary effort in the Hawaiian Islands.
Liholiho Moves Royal Center from Kailua-Kona to Honolulu
Early in 1821, Liholiho moved his court from Kailua-Kona, Hawai‘i Island to Honolulu. The royal siblings, Kauikeaouli and Nahiʻenaʻena, together with their mother, Keōpūolani and her husband Hoapili, journeyed with the chiefs to Oʻahu.
As was traditional, one of the first acts of the new mōʻī was to make a royal progression around Oʻahu to visit the people. Lilholiho’s selected route took him from Honolulu through the Koʻolau region to Waialua to “enjoy the fat mullet of Ukoʻa and to catch aholehole fish” and then by way of “Kaʻena point to Waiʻanae and then to Honolulu.” He then went to Kauai (McGregor and MacKenzie)
Liholiho Buys Cleopatra’s Barge for 1-million Pounds of Sandalwood
In the central Pacific, practically every vessel that visited the North Pacific in the closing years of the 18th century stopped at Hawai‘i for provisions and recreation; then, the opening years of the 19th century saw the sandalwood business became a recognized branch of trade.
Sandalwood, geography and fresh provisions made the Islands a vital link in a closely articulated trade route between Boston, the Northwest Coast and Canton, China.
At the same time, the Hawaiian demand for American goods was rapidly increasing, owing to the improved standards of living. The central location of the Hawaiian Islands brought many traders, and then whalers, to the Islands.
For a while, sandalwood was a medium of exchange in the Islands.
A boat named Cleopatra’s Barge arrived at Lāhainā, Maui, on November 6, 1820; the very next day Liholiho (Kamehameha II) was welcomed aboard along with some family members and attendants.
Liholiho’s father Kamehameha had loved foreign ships; over time he had collected a sizable fleet of Western vessels, which, with guns and training by the foreigners, were a major asset in unifying and maintaining his kingdom across the islands.
Liholiho inherited his father’s love of ships; one of his childhood companions remembered seeing Liholiho frequently sailing a boat model “like a real man-of-war” on a pond and also recalled that their favorite boyhood pastime was drawing ships in the sand at the beach.
Just ten days after his first visit to the ship, Liholiho purchased Cleopatra’s Barge and her cargo for 1.07-million pounds of sandalwood, worth $80,000 at the time.
On January 4, 1821, King Liholiho took formal possession of Cleopatra’s Barge, appointing his personal secretary, Frenchman Jean-Baptiste Rives, as temporary captain.
Liholiho then renamed the yacht ‘Ha‘aheo O Hawai‘i’ (Pride of Hawaiʻi.)