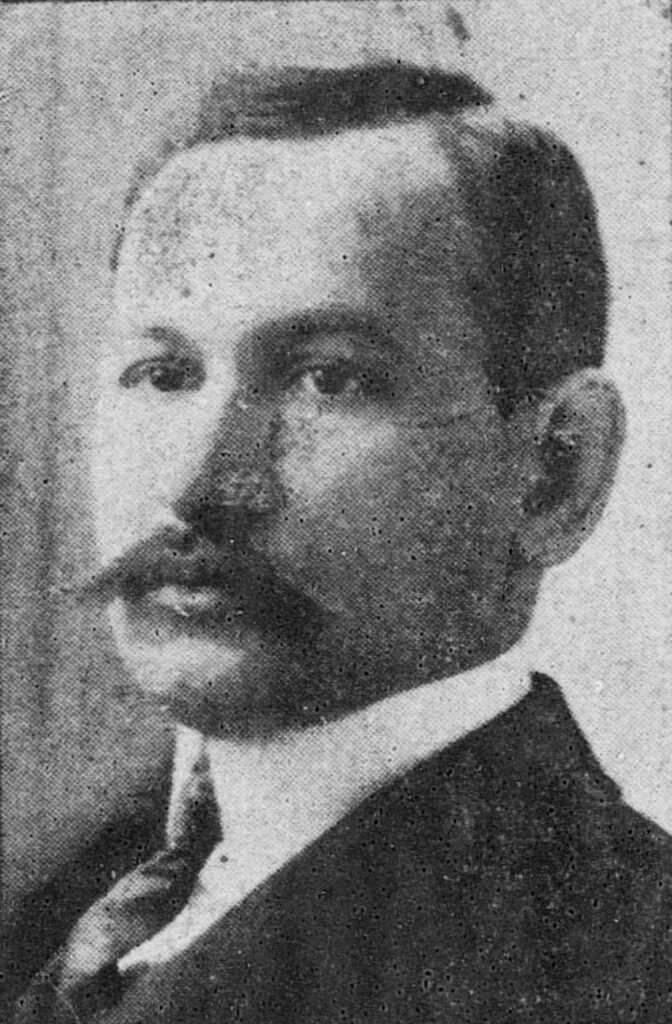Carlos (Charles) Long was from Milano, Italy. He married Julia Naoho of Maui, whose uncle, Samuel Kamakau, was one of the first Hawaiian historians.
Long was a merchant. He owned schooners. He also had several large tracts of land in Honolulu.
Julia Long had five children with Charles Long, namely: Giovoni, Carlos, Antonino, Katarina (Wright) and Elia. (Elia Long, oral history)
Carlos Appiani Long, born in Honolulu March 4, 1874 (half-Italian and half-Hawaiian), received his early education at St. Louis College and Punahou School.
He then went to Santa Clara College and received his degree from the Commerce Department. (Star Bulletin)
“He was prominent in athletics in his school days and played football on the Punahou, Maili, Town Team and other football elevens.”
“At Georgetown University, he was captain of the varsity football team in 1901, being one of the first Honoluluans to be honored in that manner in the mainland.” (Elia Long, oral history)
“While a student at the Georgetown University, Mr Long was very popular among the fellow students, and in 1898 was chosen unanimously the captain of the university football team.” (Honolulu Republican, August 8, 1901)
“Football appeals to more people than probably any other athletic game … But it is not only native born Americans who have proved themselves adepts to the game. Some of the best players on the leading teams have been foreigners.”
“Georgetown university, for instance, has for its captain this year a native of the Sandwich Islands, who was almost unanimously picked out by his fellows as the best man to the college for the honor and the responsible position.”
“He has all the natural talents of the Hawaiian race, with a soft, dreamy, gentle nature and appearance and musical inclinations. Long is a remarkably strong player and has had considerable experience in Honolulu at Oahu College”. (Logansport Pharos-Tribune, Nov 20, 1899)
“He began his law course at Stanford and later received his law degree from Georgetown University in Washington D.C. He was admitted to practice law in the courts of the District of Columbia and Hawaii.”
“He entered politics and was twice elected to the Territorial House of Representatives in 1903 and 1905. He was later appointed tax assessor for Kauai and served for eight years before returning to Honolulu in 1929.”
“For several years he was administrator for estates. He engaged extensively in the real estate business.” (Elia Long, oral history)
Carlos married Lizzie Maunakapu Whiting. They had three children Leslie, Carlos “Sonny” and Elia. Each of the children attended Punahou. (Elia Long, oral history)
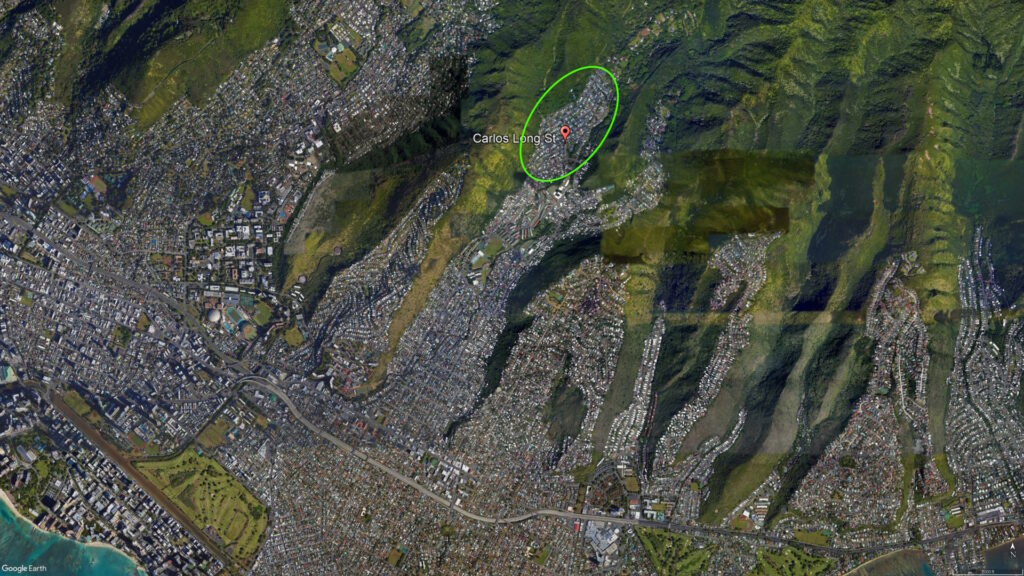
A subdivision tract and one of its main streets share the name.
“Carlos Long bought about 2,000 acres of land in Palolo. Much of the land in Palolo Valley during the 1900s was too swampy, too steep, or too remote for the development of housing subdivisions.”
Then, the Palolo Golf Course was constructed.
“The landscaping of a golf course in the 1930s enticed new residents, and the population continued to grow with the Wilhelmina Heights subdivision on Mauumae Ridge and the St. Louis Heights subdivision on Kalaepohaku Ridge.” (DEA, Cultural Surveys)
In late-1948, the first phase of a multiple phase subdivision was proposed in the back of Palolo Valley.
“The new subdivision is located in a 90 acre tract formerly owned by the Carlos Long estate. The whole tract was purchased for $350,000 by Mr. [Ruddy] Tongg and a group of associates through the American Finance Ltd.”
“Opening of a new upper Palolo valley subdivision with 125 home lots at ‘wage earners’ prices’” was announced. “Purchase price of each lot will average $3,900 … this includes the price of installing sewers, roads, sidewalks and curbs, water lines storm drains and street lights”. (Star Bulletin, December 30, 1948)
The Realtor marketing the project that the first “32 lots in the Carlos Long Palolo Valley Tract, owned by American Finance, are being placed on sale … primarily for veterans.”