Geologic evidence suggests that the modern caldera of Kīlauea formed shortly before 1500 AD. Repeated small collapses may have affected parts of the caldera floor, possibly as late as 1790. For over 300-400 years, the caldera was below the water table.
Kilauea can be an explosive volcano; several phreatic eruptions have occurred in the past 1,200 years. (Phreatic eruptions, also called phreatic explosions, occur when magma heats ground or surface water.)
The extreme temperature of the magma (from 932 to 2,138 °F) causes near-instantaneous evaporation to steam, resulting in an explosion of steam, water, ash and rock – the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens was a phreatic eruption.
The 1924 eruption at Halemaʻumaʻu documents and illustrates the explosive nature of Kilauea. However, the 1924 explosions were small by geologic standards and by the standards of some past Kilauea explosions.
The hazards of larger explosions, such as those that took place multiple times between about AD 1500 and 1790, are far worse than those associated with the 1924 series. (USGS)
There were explosions in 1790, the most lethal known eruption of any volcano in the present United States. The 1790 explosions, however, simply culminated (or at least occurred near the end of) a 300-year period of frequent explosions, some quite powerful. (USGS)
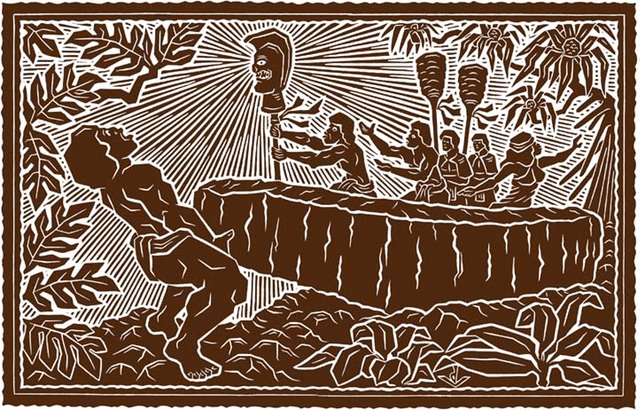
Keonehelelei is the name given by Hawaiians to the explosive eruption of Kilauea in 1790. It is probably so named “the falling sands” because the eruption involved an explosion of hot gas, ash and sand that rained down across the Kaʻu Desert. The character of the eruption was likely distinct enough to warrant a special name. (Moniz-Nakamura)
At the time, Kaʻū Chief Keōuakūʻahuʻula (Keōua) was the only remaining rival of Kamehameha the Great for control of the Island of Hawaiʻi; Keōua ruled half of Hāmākua and all of Puna and Kaʻū Districts. They were passing through the Kilauea area at the time of the eruption. The 1790 explosion led to the death of one-third of the warrior party of Keōua. (Moniz-Nakamura)
Camped in Hilo, Keōua learned of an invasion of his home district of Kaʻū by warriors of Kamehameha. To reach Kaʻū from Hilo, Keōua had a choice of two routes one was the usually traveled coastal route, at sea level, but it was longer, hot, shadeless and without potable water for long distances. (NPS)
The other route was shorter, but passed over the summit and through the lee of Kilauea volcano, an area sacred to, and the home of, the Hawaiian volcano goddess Pele. Keōua chose the volcano route, perhaps because it was shorter and quicker, with water available frequently. (NPS)
In 1919, Ruy Finch, a geologist at the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory discovered human footprints fossilized in the Kaʻū desert ash. Soon, this area of the desert became known as “Footprints.”
Barefoot walkers left thousands of footprints in wet volcanic ash within a few miles southwest of Kīlauea’s summit.
Many historians and Hawaiians believe the footprints were made by Keōua and his warriors. Keōua was known to be in the area at the time, and previous thought suggested this part of the desert did not have pre-contact use, so it was narrowed down to them.
Scientists later investigated – one approach was to look deeper at the evidence.
Forensic studies indicate that the length of a human foot is about 15% of an individual’s height. A man’s foot may be slightly more that 15%, a woman’s slightly less, but it is possible to estimate the height to a couple of inches. (USGS)
They measured 405-footprints to determine how tall the walkers were. The average calculated height is only 4-feet 11-inches, and few footprints were made by people 5-feet 9-inches or more tall. Early Europeans described Hawaiian warriors as tall; one missionary estimated an average height of 5-feet 10-inches. Many now believe that most of the footprints were made by women and children, not by men, much less warriors. (USGS)
Meanwhile, Keōua’s party was camped on the upwind side of Kīlauea’s summit – perhaps on Steaming Flat – waiting for Pele’s anger to subside. They saw the sky clear after the ash eruption and began walking southwestward between today’s Volcano Observatory and Nāmakanipaio. (USGS)
Suddenly, the most powerful part of the eruption began, developing a high column and sending surges at hurricane velocities across the path of the doomed group. Later, survivors and rescuers made no footprints in the once wet ash, which had dried. (USGS)
Then, archaeologists looked for other evidence to help identify who the footprints may have belonged to. Contrary to general thought that the area was not used by the Hawaiians, archaeological investigations discovered structures, trails and historic artifacts in the area. (Moniz-Nakamura)
Most of the features were along the edge of the Keʻāmoku lava flow. Several of the trails converge south of the flow, suggesting a major transportation network. The structures are likely temporary, used as people were traversing through the desert on their way to/from Kaʻū and Hilo. (Moniz-Nakamura)
The sheer number of temporary shelters along the Keʻāmoku flow, as well as the trail systems and quarry sites, strongly suggest that this area was frequently used by Hawaiians travelling to and through the area – before and after the 1790 eruption. (Moniz-Nakamura)
If the footprints aren’t Keōua’s warriors, then how did one-third of his warriors die?
Several suggestions have been made: suffocation due to ash; lava, stones, ash and other volcanic material; or strong winds produced by the eruption, asphyxiation and burning killed them. (Moniz-Nakamura)
A more recent suggestion is that a “hot base surge, composed primarily of superheated steam … (traveling at) hurricane velocity” was the cause of death. The wind velocity prevented the people from running away; they probably huddled together, then “hot gases seared their lungs.” (Moniz-Nakamura)
Some now suggest that, if these observations and ideas are correct, the footprints were made in 1790, but not by members of Keōua’s group. (USGS)
A reconstruction of events suggests that wet ash, containing small pellets, fell early in the eruption, blown southwestward into areas where family groups, mainly women and children, were chipping glass from old pāhoehoe. They probably sought shelter while the ash was falling. Once the air cleared, they slogged across the muddy ash, leaving footprints in the 1-inch thick deposit. (USGS)
On August 1, 1916, President Woodrow Wilson signed the country’s 13th national park into existence – Hawaiʻi National Park. At first, the park consisted of only the summits of Kilauea and Mauna Loa on Hawaiʻi and Haleakalā on Maui.
Eventually, Kilauea Caldera was added to the park, followed by the forests of Mauna Loa, the Kaʻū Desert, the rain forest of Olaʻa and the Kalapana archaeological area of the Puna/Kaʻū Historic District.
In 1961, Hawaiʻi National Park’s units were separated and re-designated as Haleakalā National Park and Hawaii Volcanoes National Park.) (Lots of good information here is from USGS, NPS and Jade Moniz-Nakamura.)