Mauna Kea, like Hawai‘i’s other older volcanoes, Hualālai and Kohala, has evolved beyond the shield-building stage, as indicated by:
- the very low eruption rates compared to Mauna Loa and Kīlauea;
- the absence of a summit caldera and elongated fissure vents that radiate its summit;
- steeper and more irregular topography (for example, the upper flanks of Mauna Kea are twice as steep as those of Mauna Loa); and
- different chemical compositions of the lava. (USGS)
Mauna Kea’s peaceful appearance is misleading. The volcano is not dead. It erupted many times between 60,000 and 4,000 years ago, and some periods of quiet during that time apparently lasted longer than 4,000 years. Given that record, future eruptions seem almost certain. (USGS Volcano Watch)
Pu‘u Kanakaleonui is one of the younger cones of the Laupāhoehoe Volcanics and is less than 13,000 years in age. (USGS) Kanaka-Leo-Nui (loud-voiced person) “was the name of a retainer of ʻUmi-a-Līloa, a chief who is said to have had a house at the top of Mauna Kea with doors facing each of the six districts of Hawaiʻi.”
“If the chief wanted the Hilo people to bring supplies, he called from the Hilo door to Kanaka-leo-nui, who shouted out the orders from the top of the hill bearing his name.” (Hawaiian Place Names)
About the time Columbus was crossing the Atlantic, ʻUmi a Līloa (‘Umi, son of Līloa), was famous in Hawaiian history for being the first aliʻi (chief) to unify Hawaiʻi Island under a singular rule.
ʻUmi was a religious chief and was known to have erected a number of ahu (shrines) throughout the ʻāina mauna (mountain lands) to make offerings to the akua. After unifying the island, ʻUmi a Līloa chose to live in the ʻāina mauna with his people rather than returning to the lower ahupuaʻa (land divisions) where kānaka typically lived.
“Umi was a trail builder …. Where the a-a was level, his men marked their way across it by smooth going. Where there were depressions in it, they were filled up to the general level, much as a modern engineer would fill them.”
“Where there were hillocks to be crossed, these were cut away if not too high and passed over in a straight line if their altitude forbade grading.” (Sol Sheridan, Mid Pacific Magazine, Oct 1912)
Pu‘u Kanakaleonui is one of the younger cones of the Laupāhoehoe Volcanics and is less than 13,000 years in age. The dark-colored deposit partly surrounding and mantling Pu‘u Kanakaleonui consists of tephra and ejecta blocks of lava mostly 10 to 50 cm in diameter but as large as 3 m long.
Some of the ejecta are from underlying lava flows that were erupted more than 65,000 years ago from the Hāmākua Volcanics. The light-colored surface below the cone consists of lava flows that are not mantled by the explosive tephra and blocks. (USGS)
The next eruption could take place anywhere on the upper flanks of the volcano. As Mauna Kea evolved from its early shield stage (equivalent to Kīlauea and Mauna Loa today) to its present post-shield stage, the volcano lost its rift zones. Consequently, the post-shield eruptions are not concentrated along narrow zones but instead are scattered across the mountain.
A prominent cinder cone will probably be constructed at each vent. The cinder cones responsible for the ‘bumpy’ appearance of Mauna Kea’s surface. The cones were built during the latest eruptive period 6,000-4,000 years ago. The next eruption will likely produce a similar cone.
For example, the most recent eruptive period, 6,000-4,000 years ago, involved eight vents on the south flank of the volcano between Kala‘i‘eha cone (near Humu`ula) and Pu‘ukole (east of Hale Pōhaku). During this same period, eruptions took place on the northeast flank at Pu‘u Lehu and Pu‘u Kanakaleonui.
Lava from Pu‘u Kanakaleonui flowed more than [12 miles] northeastward, entering the sea to form Laupāhoehoe Point. (USGS Volcano Watch)
“[Right back [of the double Hill Holei Kanakaleonui], there is a Hawaiian graveyard. They used to bury there. When they go up and make their adze, and the Hawaiians die up there, they had a little … above Kanakaleonui, in between Red Hill and Kanakaleonui.” (John “Johnny” Ah San Oral History Interview with Kepā Maly)
With the exception of the possible adze maker interments, the apparent restriction of the higher elevation burials to the apex of cinder cones is in sharp contrast to many of the burials found at Kanakaleonui, a well-known burial center located not too far outside of the Science Reserve, just below Pu‘u Mākanaka and the summit plateau.
On current evidence there are more burials in the general environs of Kanakaleonui than probably exist higher on the mountain, possibly on all of the summit plateau. (AIS Mauna Kea Science Reserve)
The disproportionate number of burials in the environs of Kanakaleonui suggests that the edge of the plateau might have been a major social boundary, with the area below reserved for commoners and the plateau for persons of higher social status (chiefs and priests).
If the very top of the cones were reserved for higher status individuals and the ground below for commoners, then Kanakaleonui must have both. (AIS Mauna Kea Science Reserve)
Laupāhoehoe is the true ‘Umi’s Trail. ‘Umikoa one, that’s when they go up and they turn around, and they meet ‘Umi Trail. (Mr. Ah San noted that Laupähoehoe-Waipunalei Trail runs up the mountain from near the heiau of ‘Umi – recorded as being named Mämala or Ha‘akoa.)
The trail runs mauka past Ke-ana-kolu (The-three-caves), which was a known resting spot on the trail up the mountain. The caves are approximately one-mile mauka from the old Keanakolu ranch house. (Maly)
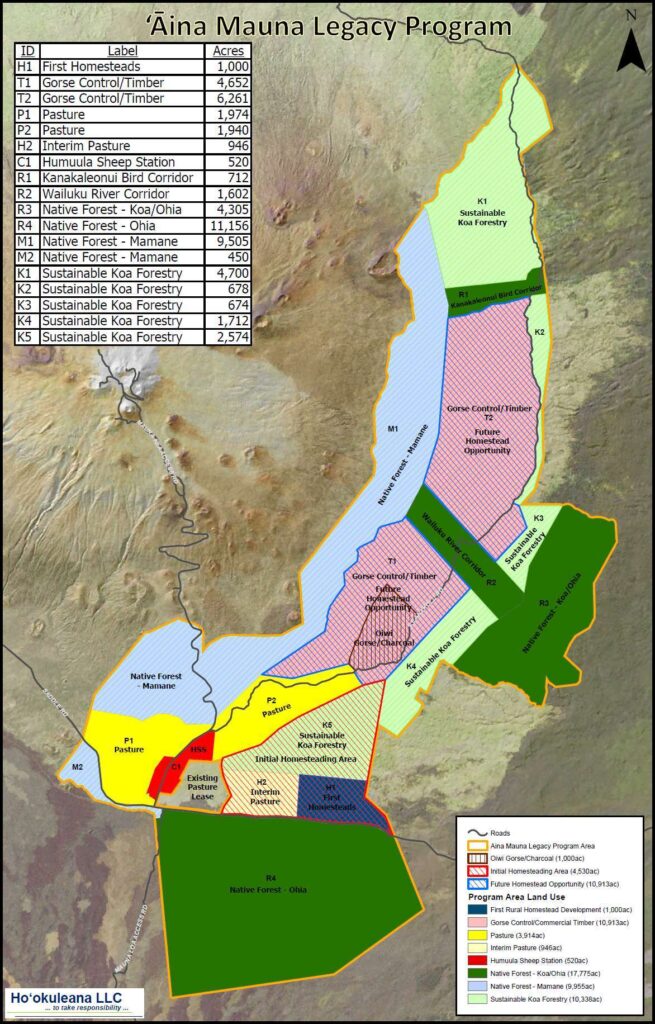
Kanakaleonui Bird Corridor (KBC), located on the east slope of Mauna Kea, is a unique transition zone from a Tropical Montane Cloud Forest to a colder, drier subalpine forest. (Pigao)
The KBC corridor is a continuous uphill slope that currently represents a gradient of woodland to grassland. The dry subalpine landscapes show sharp climate changes with small elevational changes that are easily distinguishable by the amount and type of vegetation present.
Kanakaleonui Corridor is on Department of Hawaiian Home Lands land between Mauna Kea Forest Reserve and Hakalau Forest NWR). It has many forest birds, especially ‘i‘iwi, ‘apapane, ‘amakihi, ‘elepaio, ‘akiapōlā‘au, and ‘io.
These species (and juveniles of these) are known to travel between wet forests and subalpine māmane forests during the bloom. The Kanakaleonui Bird Corridor is an interconnecting corridor for this travel. (Hawaii’s Comprehensive Wildlife Conservation Strategy)