“It began in the swimming pool at Glen Ellen. Between swims it was our wont to come out and lie in the sand and let our skins breathe the warm air and soak in the sunshine. Roscoe was a yachtsman. I had followed the sea a bit. It was inevitable that we should talk about boats.” (London)
In 1906, Jack London announced he was planning a trip on a boat – the Snark – he was to build and do blue-water sailing on a round-the-world cruise. (The Snark was named after one of Lewis Carroll’s nonsense poems.)
“‘Honolulu first,’ said London yesterday. ‘After that we are not very definite. Everybody’s in good health, the bourgeoise tradesmen have finally freed us, the boat is staunch, the weather fine. What more a man wants I don’t know.’”
“‘Meet me in Paris,’ called Mrs. Jack London back through the megaphone as the boat disappeared. ‘Isn’t it glorious? Good-by, everybody!” [April 23, 1907]
“The remaining members of the crew of the Snark are: Captain Rosco Eames, under whose personal direction the Snark was built; Herbert Stoitz of Stanford University; Martin Johnson, cook, and Hideshisa Hochigi. Cabin boy.”
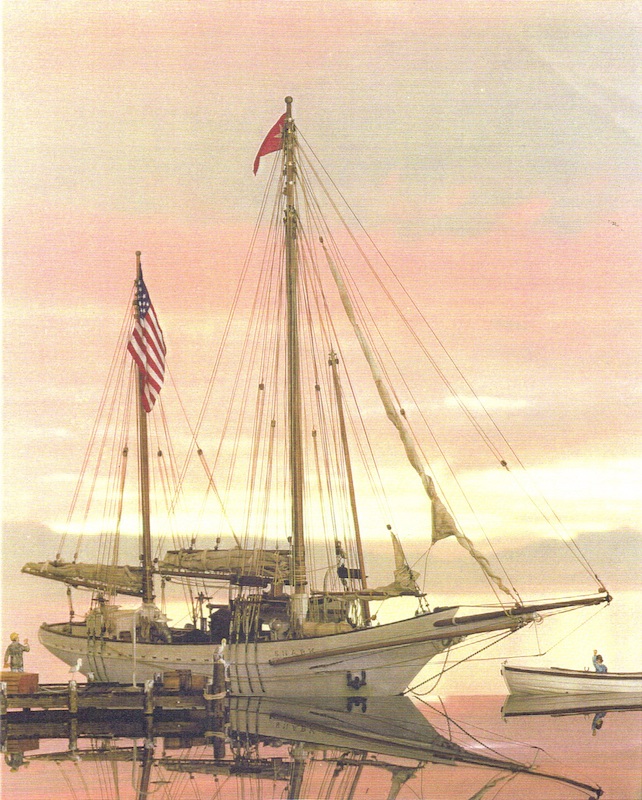
“Flying from her mainmast the red flag of Socialism, Jack London’s Snark, towed by a gasoline launch, passed through the Oakland estuary shortly after noon yesterday.”
“She had been freed from Federal surveillance and scores of the author’s friends thronged her deck as she lay at Franklin-street wharf to bid godspeed to him and his wife on their long cruise.”
“Cheer after cheer rent the air as the Snark moved down the channel and passed out into the bay, on her way to Bonita Cove, near Sausalito, where she will await the ebb tide this morning before sailing through the Golden Gate.”
“In the farewell levee on the deck leaders in Socialism hobnobbed with literary workers and a staid burgher friend or two mingled in the gathering with men of the professions. But for the most part the throng that gathered was made up of workingmen as negligee in attire as the author himself.”
“They all called him ‘Jack,’ and he seemed to know them all. They cheered when the two banners of red, the one bearing the initial S. for Snark and Socialism: the other, a black and white star, the London emblem,” were hauled by Captain Eames to the masthead.”
“There they will fly until the cruise is done, carrying the message of Socialism to the people of the seven seas.” (PCA, April 30, 1907)
“The arrival of Mr. Jack London in the Snark is looked forward to with pleasant anticipation by certain society folk who will doubtless wine and dine him most hospitably.”
“After many rumored departures, he is said to have really sailed from San Francisco and may be expected here shortly, wind, weather and his navigating officer permitting.” (PCA, April 28, 1907)
“Folks flocked down to the waterfront to get a glimpse of the little craft which was designed to circumnavigate the globe.”
“A glimpse was all they got, for the Snark gave a line to Young Brothers’ tug Waterwitch and was towed to Pearl Harbor, where she dropped anchor off the Hobron place, and will probably remain there for the best part of the next two months.”
“Mr and Mrs London made up their respective and collective minds to spend at least two months in the waters of Pearl Lochs and to take their residence ashore in the TW Hobron cottage. They yearn for the shore awhile and want to be quite.”
“‘We are here for work,’ said Mrs London when the Londons were visited by a representative of the Star shortly after their arrival here at 11:20 o’clock this morning [May 20, 1907]. Continuing Mrs. London stated that her husband intended to put in a lot of time writing and that they could not Image a quieter place than Pearl Lochs.”
“They will not go to Honolulu today. They do not want the distractions of the city, preferring, for the present at least, the peacefulness of the Hobron cottage, whither the typewriter has already been transferred from the cabin of the Snark and where
its click will be heard until late in July.”
London noted, “‘Pearl Harbor is a dream. The coming through the breakers into the placid water of the lagoon is a sight I shall never forget. We shall remain here and work as quietly as may be. I’m sick of the hotels and steamships.’”
“There are years of adventure and romance before the people of the Snark and the beginning has been auspicious. The Snark has proved herself to be everything that London claimed she would be.”
“‘We’ve come 2600 miles In twenty-seven days,’ said the captain, ‘and while not tired of the trip must say that land looks mighty good to me. We went south in order to fall in with the dolphins and flying fish and latterly bore southwest for the wind as far as the nineteenth longitudinal.’”
“‘We loafed along the whole way, with more wind the first four days out than we had all the rest of the trip. The voyage was singularly devoid of Incident. Three days out a ship was sighted, after which nothing was seen till Sunday, when we saw a steamer hull down.’
“The Snark is thirty tons gross and ten tons net; fifty-one feet in length, fifteen and five-tenths beam and seven and fieve-tenths in depth of hold. Her foremast is much taller than the main and she carries a big bowsprit. Her deck is flush and living apartments occupy the whole vessel from stem to stern.”
“The Snark, according to present plans, will leave here in about twenty days for Hilo. From Hilo the South Seas, Australasia and the Orient, and the rest of the world, will be checked off the Snark’s chart.” (Hawaiian Gazette, May 21, 1907)
Charmian London (Mrs Jack London) made a couple of books about the two years’ with her husband in the forty-five-foot ketch Snark into the South Seas, by way of the Hawaiian Islands.
The seafaring portion of her notes was published in 1915 as “The Log of the Snark.” The record of five months spent in the Paradise of the Pacific, Hawaii, she made into another book, “Our Hawaii,” issued in 1917. Jack London had previously passed through Honolulu in 1893.
The South Sea trip was meant to be just the beginning of the cruise. London dreamt of threading the Arabian Sea and traversing the Mediterranean and the Atlantic but ultimately it was the savage climate of the south Pacific that did for him.
After about 2-years of sailing, at Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands London became afflicted by a skin disease which meant his hands swelled up and chunks of skin fell off. Without his hands he could not write and earn the money to fund the voyage and, after seeking medical advice, he was urged to abandon the trip.
It was a devastating decision for London, and he and Charmian were distraught, as Jack recalled: “In hospital when I broke the news to Charmian that I must go back to California the tears welled into her eyes.”
“For two days she was wrecked and broken by the knowledge that the happy, happy voyage was abandoned.” Thus one of the most offbeat and pioneering cruises ended rather abruptly. Once the voyage was called off, Snark was sailed to Sydney and sold there. (Jefferson)