“The village with the walled pond and grove of hau and coconut trees was Kahalu‘u, and Kahalu‘u-kai-ākea was the chief who controlled the ahupua‘a which bears his name.”
“He was the father of the beautiful, glowing-skinned chiefess, Mākole‘ā. The beauty of Kahalu‘u is described with the saying “Kahalu‘u ua ‘āina ala i ka wai puka iki o Helani” (Kahalu‘u is the land [known for] the small rising waters of Helani.)”
“At Kahalu‘u, Hale‘ōpele was the āhua (hillock-agricultural feature) covered with coconut trees…”
“…A hō‘ea i ke kuono iloko he ‘ili‘ili wale no ke one, a ke kai e po‘i ana me ka ho‘omaha ‘ole o nā Keauhou ia — And when you arrived at a bay with pebbly sand, where the ocean continuously laps upon the shore it was Keauhou…”
“A komo mai la ‘olua i ka ulu ‘ōhi‘a o nä Keauhou ia, o ka ulu ‘ōhi‘a o Moku‘aikaua — and when you entered the ‘ōhi‘a grove in the lands of Keauhou, it was the ‘ōhi‘a grove of Moku‘aikaua…” (Ka Hōkū o Hawai‘i, April 9, 1914, Maly)
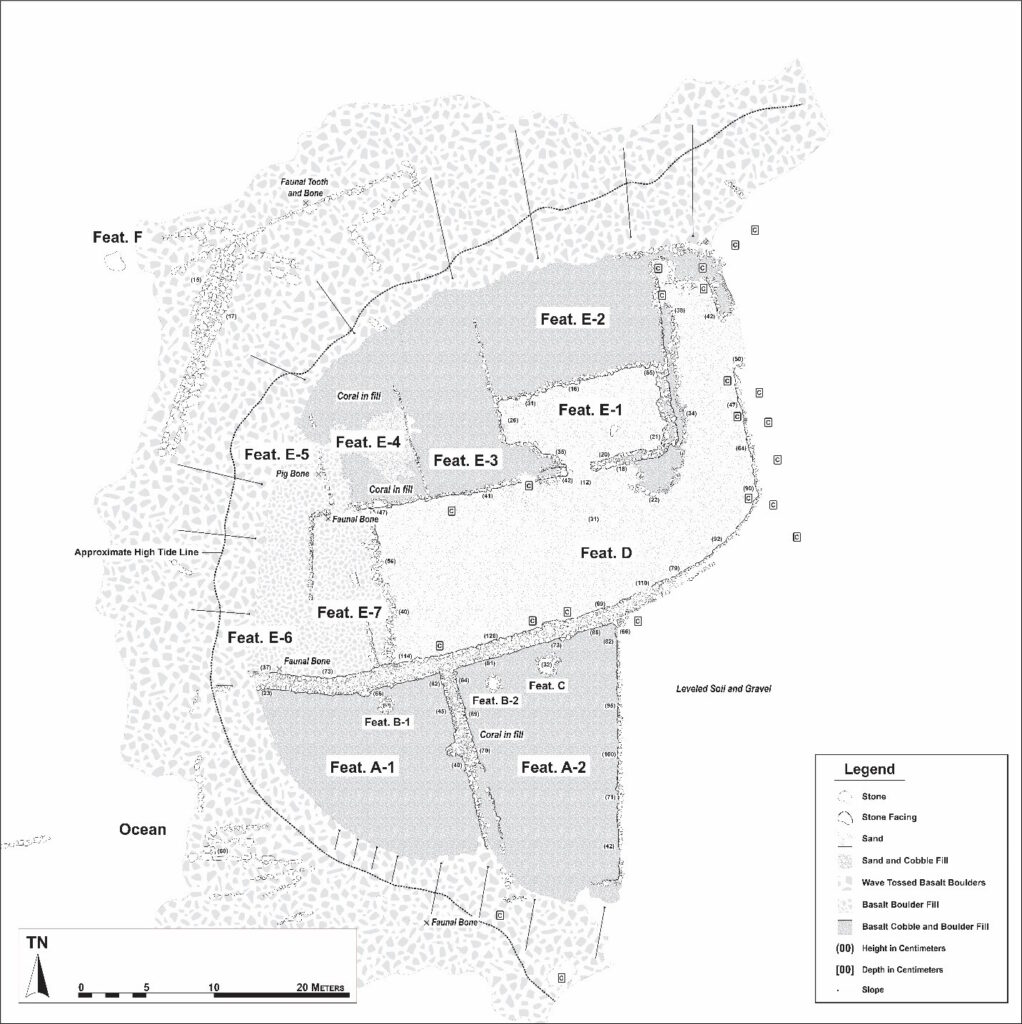
At Kahalu‘u is Kapuanoni Heiau … “Only portions of walls could be traced, 97 feet apart; one of them, a wall foundation, could be followed for 40 feet, and the other, a standing wall 4.5 feet wide, was distinguishable for 34 feet. The place had the appearance of having been much disturbed in early times.”
“It is now overgrown with hau. Local information, from the grandson of its last priest, was that the heiau was built by Kalani‘ōpu‘u and that it was for prayers in general.” (Stokes, 1906) It was “a temple dedicated to agricultural and fishing success.” (NPS)
Thrum (1908) describes Kapuanoni as “a large heiau of Kahaluu, described as an ancient puuhonua and luakini, built in the time of Lono.”
“Tradition has it that when Malaihi was its kahu (or keeper), a native fled to it from Pahoehoe and was followed in by his pursuers, seized, and taken away without remonstrance, which violation coming to the ears of the king he had the keeper slain and sacrificed on the altar of Ohiamukumuku.”
The name “ka pua noni” can be translated literally as ‘the’ (ka) ‘noni flower’ (pua noni). The deeper kaona (meaning) behind this place name has not been passed on. (SWCA)
Kapuanoni is situated on the promontory that forms the southern headland of Kahaluʻu Bay and is surrounded by water on three sides. The heiau formed an integral component of the chiefly and religious compound of coastal Kahalu‘u during the traditional period. (SWCA)
Subsequent to c. 1730s, the chiefs Alapa‘i, Kalani‘ōpu‘u, and Kamehameha I, are all associated with residency and activities in this region of Kona, with specific references to Kahalu‘u and Keauhou. (Maly)
“The years 1775, 1776, 1777, 1778, and 1779. Kalaniopuu went to war at Kaupo on Maui, with his Alii, his war Officers, and his soldiers. Kalaniopuu first went to war at Kaupo …” (Kuakoa, Dec 8, 1866)
“Ka-lani-‘opu‘u returned to Hawaii embittered against Ka-hekili by the realization of his defeat, and spent a year in preparing an army made up of a body or men from each of the six districts of the island, each division led by a warrior chief.” (Kamakau)
“Six army corps or brigades were organised, and became known by the names of I, Ahu, Mahi, Palena, Luahine, and Paia; the members of the royal family were formed into a life-guard, called Keawe; and the Alii-ai-alo – the nobles who had the privilege of eating at the same table with the Moi – composed two regiments called Alapa and Piipii.”
“While thus preparing material resources, Kalaniopuu was not forgetful of his duties to the god whom he acknowledged and whose aid he besought. This god was Kaili – pronounced fully ‘Ku-kaili-moku’ – who, from the days of Liloa, and probably before, appears to have been the special war-god of the Hawaii Mois.” (Fornander)
“[H]e repaired and put in good order the Heiaus called ‘Ohiamukumuku’ at Kahaluu, and ‘Keikipuipui’ at Kailua, in the Kona district, and the high priest Holoae was commanded to maintain religious services and exert all his knowledge and power to accomplish the defeat and death of the Maui sovereign.” (Fornander) Kalani‘ōpu‘u is also credited with building the heiau of Kapuanoni, presumably during this time. (Maly)
At the time of Captain James Cook’s arrival (1778-1779), the Hawaiian Islands were divided into four kingdoms: (1) the island of Hawaiʻi under the rule of Kalaniʻōpuʻu, who also had possession of the Hāna district of east Maui; (2) Maui (except the Hāna district,) Molokai, Lānai and Kahoʻolawe, ruled by Kahekili; (3) Oʻahu, under the rule of Kahahana; and at (4) Kauai and Niʻihau, Kamakahelei was ruler.
When Cook arrived on the Island of Hawai‘i (1779), Kalaniʻōpuʻu was on the island to Maui to contend with Kahekili, king of Maui. The east side of Maui had fallen into the hands of Kalaniʻōpuʻu and Kahekili was fighting with him to gain control.
Kalaniʻōpuʻu returned to Hawaiʻi and met with Cook on January 26, 1779, exchanging gifts, including an ʻahuʻula (feathered cloak) and mahiole (ceremonial feather helmet.) Cook also received pieces of kapa, feathers, hogs and vegetables.
“After Captain Cook’s death [in 1779] Kalaniopuu dwelt some time in the Kona district, about Kahaluu and Keauhou, diverting himself with Hula performances, in which it is said that he frequently took an active part, notwithstanding his advanced age. “
“Scarcity of food, after a while, obliged Kalaniopuu to remove his court into the Kohala district, where his headquarters were fixed at Kapaau.” (Fornander)
“During the period of his rule, between c. 1782 to 1819, Kamehameha I was noted for his dedication to his gods and their kapu. Kamakau records that Kamehameha I dedicated the heiau of Kama-i-ke‘e-kū and ‘Ōhi‘a-mukumuku in Kahalu‘u to his war god.”
“In Thrum’s account of Hawaiian temples, readers are told that Kamehameha also built the heiau named Hāpaiali‘i shortly after the battle at Moku‘ōhai in c. 1782. It was through the battle of Moku‘ōhai at Ke‘ei, that Kamehameha I secured a portion of the island of Hawai‘i under his rule.”
“Also, following the death of Kalani‘ōpu‘u the lands of Kahalu‘u and the “two Keauhou” were among those divided between the chiefs.”
“Among the most important ali‘i of the Kamehameha I period associated with Keauhou and Kahalu‘u, was the chiefess Keōpūolani, known in her youth as Wahinepio. She was raised at Keauhou, where she lived until ca. 1795.”
“The daughter of Kïwala‘ō, she was also the sacred wife of Kamehameha I, and mother of the children who succeeded him in rule.” (Maly)
“Kuakini was born in 1791, while his parents lived at Kahalu‘u and Keauhou. Kuakini was a younger brother of Ka‘ahumanu, the favored wife of Kamehameha I, and regarding the birth of Kuakini, and his tie to the lands of Kahalu‘u and Keauhou, Kamakau, recorded that:”
“At the birth of the child [Kuakini] there was a great hula at Kaha-lu‘u, and the name hula (hula inoa) was being danced for the birth of the new son to Na-mahana and Ke‘e-aumoku.”
“Visitors came to bring gifts (ho‘okupu), and among them was Ka-mehe-‘ai-ku who had gone away and hidden in the country and slept with a man and given birth to a child.”
“She was a cousin of Ke‘e-au-moku, and when she was discovered among the spectators at the hula Ke‘e-au-moku gave the child to her to suckle and gave with him the land of Keauhou; and Ka-mehe-‘ai-ku took the little chief to Keauhou and there nourished him until he was grown…” (Kamakau, Maly)
“In 1931, a visitor to nearby Keauhou Bay described Kahalu‘u as ‘miles off the beaten path … a place where people used to live in numbers and now live no more’ (Schench). By the 1950s, the area was mostly abandoned and heavily overgrown”
“In 1970, the Outrigger Keauhou Beach Hotel was constructed just inland of Kapuanoni Heiau. The heiau was situated directly adjacent to the hotel pool.” (SWCA) (The demolition of the Keauhou Beach Hotel was completed in August 2018.) (KSBE)
While some of the walls of the heiau complex remain, the seaward edges of the structure have been badly damaged by high surf events while its interior has been modified by various additions and reconstruction efforts undertaken when it formed part of the grounds of the Outrigger Keauhou Beach Resort.
In 2005, the trustees of Kamehameha Schools decided to restore the five coastal heiau of Kahalu‘u, including Kapuanoni. Restoration of two heiau (Ke‘ekū and Hāpaiali‘i) was completed in 2009. Restoration of Makoleā followed that and planning and activities to restore Kapuanoni and Po‘o Hawai‘i pond are underway.
Drone flyover of Kapuanoni: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fxsRxa1pimA&t=1s (SWCA)