In 1876, the legislature passed “An Act for the Protection and Preservation of Woods and Forests” in response to water crisis in Honolulu due to deforestation and decrease in stream flow Nuʻuanu Stream, the main source of water for Honolulu.
In 1882, the first government tree nursery was established to provide tree seedlings for reforestation of mauka lands above Honolulu. 50,000 tree seedlings are planted on the denuded slopes of Tantalus (Honolulu). (DLNR-DOFAW)
In 1903, the Hawaii Territorial Legislature passed Act 44 establishing the Board of Agriculture and Forestry, predating the USDA Forest Service by one year. Act 44 expanded on the Forestry Act of 1876 and provided the legal vehicle for the creation of reserves encompassing private as well as public lands.
The Forest Reserve System was created by the Territorial Government of Hawai’i through Act 44 on April 25, 1903. It was cooperative arrangement between the Hawai‘i Sugar Planters Association and the territorial government.
Plantations needed wood for fuel, but they also needed to keep the forests intact to draw precipitation from the trade winds, which in turn fed the irrigation systems in the cane fields below. (DLNR-DOFAW)
The first Territorial forester, Ralph S Hosmer, suggested that the forest had been declining in the uplands as a result of fire, grazing and insects. In order to preserve the forest, it was necessary to keep the ungulates out. From 1924 to 1926 hundreds of thousands of pigs, sheep, cattle and goats were reportedly removed from Hawaii’s Territorial forests.
But the planters were also worried about hunters in the woods starting fires from their camps. Likewise, the commercial ranchers were also wary of individual hunters who could also shoot cattle from the ranch. (Peter Mills)
Then the US economy took a hit … after a decade of national prosperity in the Roaring Twenties, Americans faced a national crisis after the Crash of 1929. The Great Depression saw an unemployment rate of more than twenty-five percent in the early 1930s. (pbs)
As a means to make work Franklin Delano Roosevelt authorized the New Deal; the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) succeeded the Emergency Conservation Work agency, which started in 1933. In 1939, the CCC became part of the Federal Security Agency. (It was eliminated in 1943.) (UH Mānoa)
The purpose of the CCC and its predecessors was to provide employment in forestry and conservation work. It “brought together two wasted resources, the young men and the land, in an effort to save both.” (NPS)
From FDR’s inauguration on March 4, 1933, to the induction of the first CCC enrollee, only 37 days had elapsed. The goals of the CCC according to the law were: “1) To provide employment (plus vocational training) and 2) To conserve and develop ‘the natural resources of the United States.’”
By the end of the third year, there were 2,158-CCC camps in the nation and 1,600,000-men had participated in the program. (NPS)
There were five primary CCC camps built in Hawaiʻi (the CCC Compound at Kokeʻe State Park, the most intact today; what is now a YMCA camp at Keʻanae on Maui; a research facility on the Big Island; Hawaiian Homes Property with only two buildings remaining on the Big Island; and part of Schofield Barracks in Wahiawa on Oʻahu.) Other temporary campgrounds were spotted in work areas around the Islands. (NPS)
While the first 57 CCC enrollees on Hawaiʻi Island began working in 1934, it was not until June of 1935 the first CCC camp was established (in Hawai‘i National Park – as Hawai‘i Volcanoes National Park was originally called), which housed 200 enrollees.
The territorial foresters’ camp at Keanakolu was expanded into a Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) field camp. All of these buildings are still standing today.
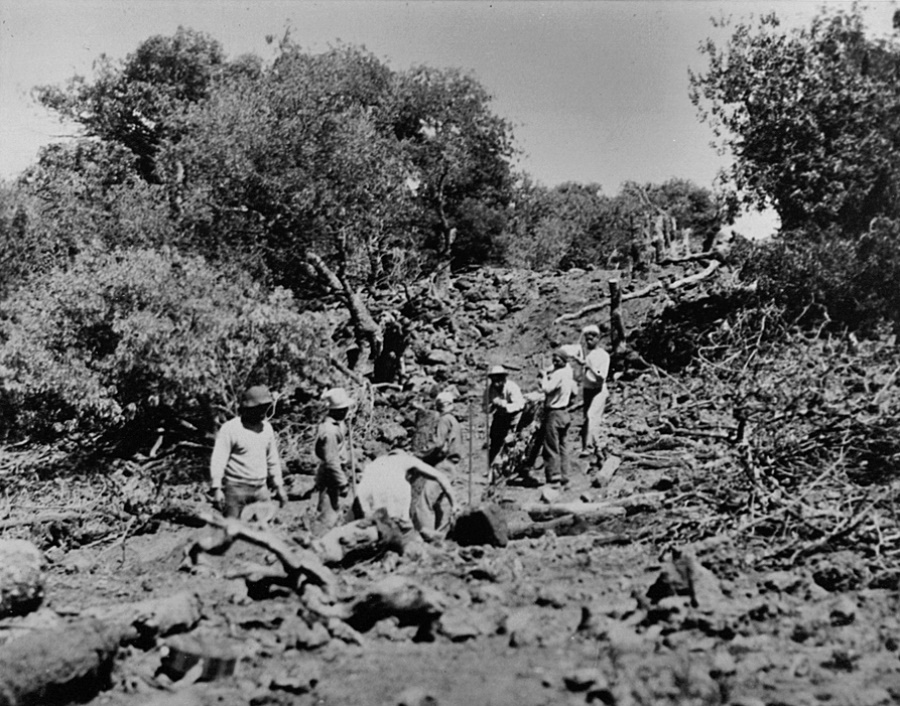
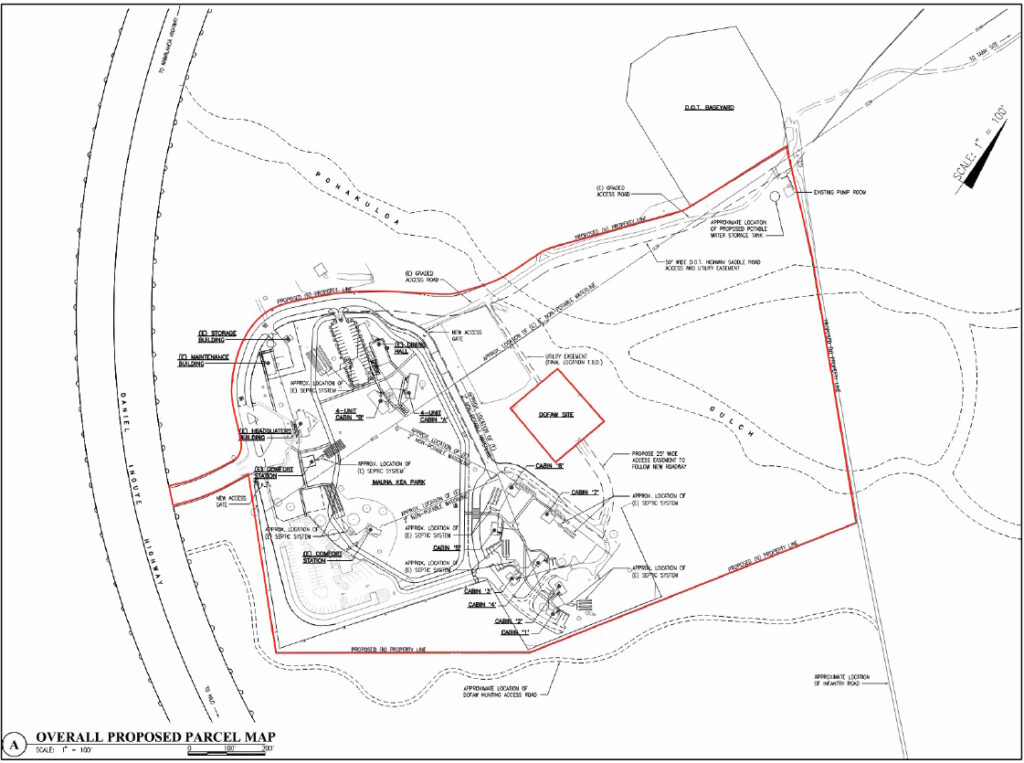
Additional camps were also constructed around Mauna Kea Forest Reserve boundaries to house crews of CCC enrollees. In 1935, a CCC camp was at Pōhakuloa. It included a cluster of buildings and tents that included a recreation/ dining hall, two bunkhouses, two cottages, seven cabins, and seven outbuildings.
Pu‘u Pōhakuloa is a cinder cone overlooking the PTA headquarters area on the Saddle Road. Pōhakuloa means long stone. It also refers to a deity of the forest lands that extended across Mauna Loa towards Mauna Kea. Pōhakuloa, the deity, was a form of the akua Kū, a lover of Poliʻahu, a patron of canoe makers, and in his human form an ʻolohe expert and woodworker,
The hill gives its name to the respective Pōhakuloa references in this area. One early name was associated with a Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) camp in this area.
The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) undertook fencing, road building and visitor facilities on Mauna Kea. The CCC built a stone cabin at Hale Pōhaku, which gained its name (house of stone) from that structure. The cabin at Hale Pōhaku provided a shelter for overnight hikers, hunters and snow players.
In 1935-36, as part of the effort to eradicate wild sheep from the mountain, the CCC took on the project of building a fence around the Mauna Kea Forest Reserve (over 60 miles of fencing). Sheep drives were then carried out in an attempt to eliminate the sheep from the reserve.
The CCC brought water down to Pōhakuloa from a mountain spring … “The CCC days … Up the gulch, up on the mountain, remember, they tapped one of the springs up there …”
“Yes, they had one of the pipes going up. You can see the pipe when you go, it’s coming down.” (Jess Hannah; Maly) “[T]hat water for Pōhakuloa, there’s a spring, Hopukani Spring. CCC boys built the pipeline.” (Davd Woodside; Maly) The spring provided a “continuous supply of pure water.” (Bryan; ASM) (Spring water is no longer used; water is trucked in from Hilo or Waimea.)
The advent of World War II brought an end to the CCC program, as the remaining manpower and funding for the program were redirected toward the war effort.
By July 1, 1942, all Territory of Hawaiʻi CCC camps were closed, transferred to the military, or abandoned. The Army operated Camp Pōhakuloa between 1943 and 1945. The army also took over the old CCC camp house at Pōhakuloa and used it during the war.
After the end of the CCC programs and World War II, the old CCC facilities at Pōhakuloa were primarily used by staff of the Territorial Divisions of Forestry, Fish and Game including lodging by sheep and bird hunters or by other members of the public seeking recreational accommodations.
“Sheep hunters usually gather at Pohakuloa, the lodge maintained by the Hawaiian Board of Forestry and Agriculture. Here they spend the night under piles of blankets (because of the 6,500 foot elevation, the nights are almost always cold) and start out before sunrise for the mountain ridges.”
“They climb to the ten thousand foot elevation, where wild sheep and goats are in abundance. The Board of Forestry encourages hunting, as the animals have caused serious erosion by eating vegetation, and some authorities believe that the sheep and goats will never be entirely exterminated.”
“In its desire to provide hunting facilities, the Territory maintains not only Pohakuloa lodge, with its bedding accommodations for fifty people, but smaller lodges at Kemole and Kahinahina.” (Paradise of the Pacific, May 1948; Maly)
In 1954, the Division of Territorial Parks was created, and the former CCC facilities became part of Pōhakuloa Park, also called “Pohakuloa Hunting Lodge”.
The division began a series of improvements that would eventually replace the existing CCC cabins with all new buildings. (No physical evidence of the original CCC structures remain, as they were removed by 1968.)
In August 1962, DLNR’s Division of State Parks officially assumed all responsibility for administering these facilities and booking overnight accommodations. Forestry, Fish and Game staff continued to use a number of older structures.
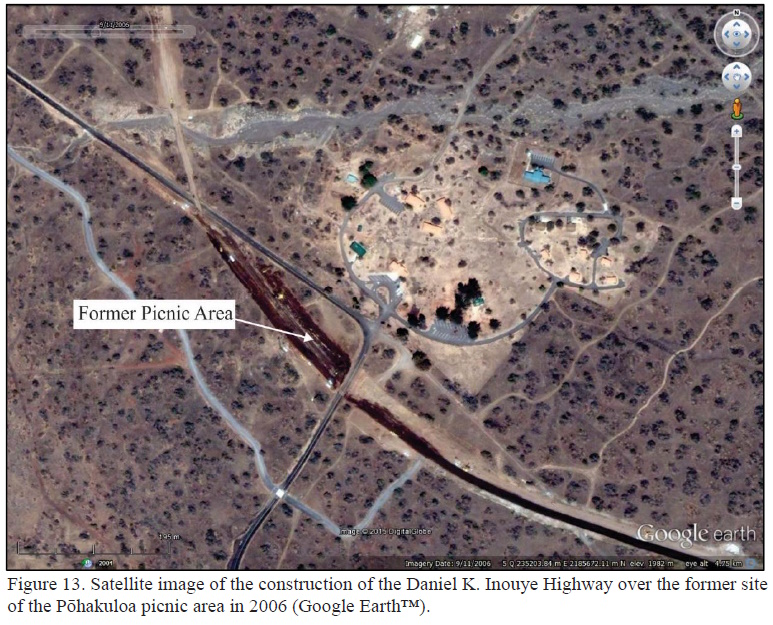
The transformation of the Pōhakuloa CCC camp into the Pōhakuloa Park and later Mauna Kea State Recreation Area happened between 1961 and 1970.
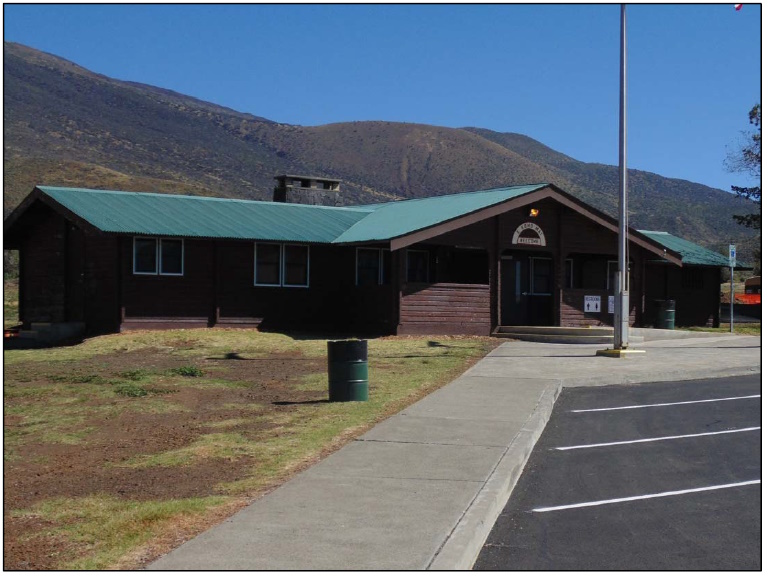
The first of these improvements was a picnic area south of the Saddle Road from the CCC cabins. In 1961, major improvements to the Park began with the addition of new cabins. The first three cabins, variously called the “Housekeeping,” “Family,” or “Vacation” cabins, were built northeast of the former CCC complex, followed by two more the following year.
These five identical cabins, built on post-and-pier foundations, were prefabricated cedar structures manufactured by Loxide Structures of Tacoma, Washington. The cabins were roofed with cedar shakes and were replaced with corrugated metal in 1989.
Each of these cabins was named after a native Hawaiian plant as illustrated by a wooden plaque near its door with the plant name. In 1963, the existing comfort station was built, using a combination of fir, pine, and hollow tile.
A new headquarters building, caretaker’s cabin, and a storage building were constructed. Each of these were pre-fabricated by Pan-Abode Company in Washington State. The buildings are tongue-in-groove cedar log cabins built on post-and-pier foundations and roofed with cedar shakes.
The two “Family” cabins (now the ADA accessible cabins) were also built near the cluster of vacation cabins on the other side of the recreation area. These cabins, like the other new buildings, were prefabricated tongue-ingroove cedar kit cabins supplied by the Pan-Abode Company.
With the construction of the Comfort Station, the park’s picnic area was relocated from south of Saddle Road to its present location.
At its meeting on March 28, 2014, BLNR approved the management transfer of the State Park to the Department of Parks and Recreation, County of Hawai‘i; and approved the withdrawal of the park area from the Mauna Kea Forest Reserve and set aside to the County for park purposes.
The park was renamed Gilbert Kahele Recreation Area in 2019. The late Hawai‘i Island State Senator, Gilbert Kahele, “worked just down the road from the recreation area for 34 years as Director of the Public Works Division at the Pōhakuloa Training Area.”
“When he served in the state legislature he was instrumental in achieving park improvements by way of the transfer of the management to Hawai‘i County.” (Kahele; DLNR Release) Lots here is from Cultural Surveys, ASM and Rosendahl.)