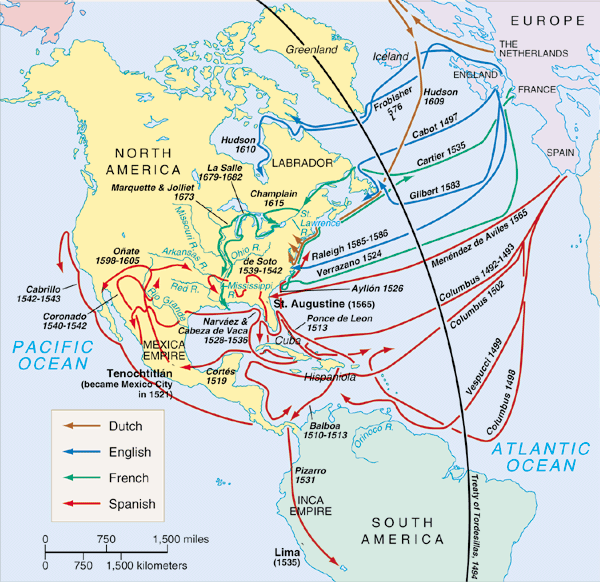
After numerous conquests by the Spanish and French, in 1578 Humphrey Gilbert, the author of a treatise on the search for the Northwest Passage, received a patent from Queen Elizabeth to colonize the “heathen and barbarous landes” in the New World which other European nations had not yet claimed. It would be five years before his efforts could begin. When he was lost at sea, his half-brother, Walter Raleigh, took up the mission.
In 1585 Raleigh established the first British colony in North America with a group of colonists (91 men, 17 women and nine children) on Roanoke Island off the coast of North Carolina. The first act was to restore to their friends the two Indians who had been previously taken to England.
The colony was later abandoned. Sir Walter Raleigh fitted out another colony, which sailed in the spring of 1587; the second effort also proved a failure. Mysteriously, by 1590 the Roanoke colony had vanished entirely. Historians still do not know what became of its inhabitants.
The failure that attended all these efforts of the hopeful and energetic Raleigh was probably due, if not wholly, to the fact that he did not himself accompany and command any of his expeditions. And, the main reason that he did not go with the ships was, that he was a great favorite with Queen Elizabeth, and she was not willing to let him risk himself in such adventures. (Johnson)
British First Success at Jamestown
It would be 20 years before the British would try again. This time – at Jamestown in 1607 – the colony would succeed, and North America would enter a new era. (Alonzo L Hamby)
The early 1600s saw the beginning of a great tide of emigration from Europe to North America. Spanning more than three centuries, this movement grew from a trickle of a few hundred English colonists to a flood of millions of newcomers. Impelled by powerful and diverse motivations, they built a new civilization on the northern part of the continent.
Most European emigrants left their homelands to escape political oppression, to seek the freedom to practice their religion, or for adventure and opportunities denied them at home.
In 1606, King James I divided the Atlantic seaboard in two, giving the southern half to the London Company (later the Virginia Company) and the northern half to the Plymouth Company.
Just a few months after James I issued its charter, the London Company sent 144 men to Virginia on three ships: the Godspeed, the Discovery and the Susan Constant. They reached the Chesapeake Bay in the spring of 1607 and headed about 60 miles up the James River, where they built a settlement they called Jamestown.
Then, the first English emigrants to what would become the New England colonies were a small group of religious separatists, later called the Pilgrims, who arrived in Plymouth in 1620 on the Mayflower to found Plymouth Colony.
Ten years later, a wealthy syndicate known as the Massachusetts Bay Company sent a much larger (and more liberal) group of Puritans to establish another Massachusetts settlement. With the help of local natives, the colonists soon got the hang of farming, fishing and hunting, and Massachusetts prospered. As the Massachusetts settlements expanded, they generated new colonies in New England.
Between 1620 and 1635, economic difficulties swept England. Many people could not find work. Even skilled artisans could earn little more than a bare living. Poor crop yields added to the distress. In addition, the Industrial Revolution had created a burgeoning textile industry, which demanded an ever-increasing supply of wool to keep the looms running. Landlords enclosed farmlands and evicted the peasants in favor of sheep cultivation. Colonial expansion became an outlet for this displaced peasant population.
Later, more came and expansion was occurring across the Eastern Seaboard.
By 1750, some 80 per cent of the North American continent was controlled or influenced by France or Spain. Their presence was a source of tension and paranoia among those in the 13 British colonies, who feared encirclement, invasion and the influence of Catholicism.
In 1700, there were about 250,000 European settlers and enslaved Africans in North America’s English colonies. By 1775, on the eve of revolution, there were an estimated 2.5 million. The colonists did not have much in common, but they were able to band together and fight for their independence.
The American Revolutionary War (1775-1783) was sparked after American colonists chafed over issues like taxation without representation, embodied by laws like The Stamp Act and The Townshend Acts. Mounting tensions came to a head during the Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775, when the “shot heard round the world” was fired.
It was not without warning; the Boston Massacre on March 5, 1770 and the Boston Tea Party on December 16, 1773 showed the colonists’ increasing dissatisfaction with British rule in the colonies.
The Declaration of Independence, issued on July 4, 1776, enumerated the reasons the Founding Fathers felt compelled to break from the rule of King George III and parliament to start a new nation. In September of that year, the Continental Congress declared the “United Colonies” of America to be the “United States of America.”
France joined the war on the side of the colonists in 1778, helping the Continental Army conquer the British at the Battle of Yorktown in 1781. The Treaty of Paris ending the American Revolution and granting the 13 original colonies independence was signed on September 3, 1783. (History-com)
Here is a list of the thirteen colonies (now states) with the year they were founded: Virginia (1607); New Hampshire (1623); Massachusetts (1630); Maryland (1633); Connecticut (1636); Rhode Island (1636); Delaware (1638); North Carolina (1663); South Carolina (1663); New York (1664); New Jersey (1664); Pennsylvania (1681) and Georgia (1732).
Vermont, which was not one of the 13 colonies, is named because, after seeing the Green Mountains, French explorer Samuel de Champlain referred to it as “Verd Mont” (green mountains) on a map in his native French.
Click the following link to a general summary about the Thirteen Colonies:
https://imagesofoldhawaii.com/wp-content/uploads/Thirteen-Colonies.pdf




Leave your comment here: