“We therefore recommend again and again, to the curious investigators of the stars to whom, when our lives are over, these observations are entrusted, that they, mindful of our advice, apply themselves to the undertaking of these observations vigorously.”
“And for them we desire and pray for all good luck, especially that they be not deprived of this coveted spectacle by the unfortunate obscuration of cloudy heavens, and that the immensities of the celestial spheres, compelled to more precise boundaries, may at last yield to their glory and eternal fame.” (Sir Edmond Halley (1656-1742))
Venus orbits the Sun within Earth’s orbit, so it occasionally happens that as seen from Earth, the disk of Venus passes across the Sun. It appears as a diminutive black spot, barely 1/30th the diameter of the Sun. With the right atmospheric conditions to soften the intense sunlight, an unobstructed horizon, and enough advance warning, a keen eye can spot the transit at sunrise or sunset. (LOC)
There have been fifty-two transits of Venus across the face of the Sun since 2000 B.C., but until 1643 A.D., no human was known to have observed this astronomical rarity. (LOC)
“History says that Jeremiah Horrocks was the first human to ever witness a transit by Venus in 1639, but could other more ancient people have also seen it too?” (Odenwald)
In 1769 Benjamin Franklin published an article in the journal of the Royal Society of London presenting the transit of Venus observations of Messrs. Biddle and Bayley.
Some historians credit this account from pre-revolutionary America as the first occasion on which American science went on display before the international community. (LOC)
Astronomers quickly discovered that by measuring the transit, the distance from the Sun to Earth could be calculated.
In 1761, the exact value of this number was still unknown; estimates ranged from 5 million to over 150 million miles. Without its precise value, astronomers could not deduce the physical size of our solar system, or the dimensions of the universe beyond the solar system’s outer reaches. The size, mass, and radiant power of our Sun were also left ill-defined. (LOC)
In May 1768 James Cook was promoted to the rank of lieutenant and given command of the bark Endeavour. He was instructed to sail to Tahiti to observe the transit of Venus and also to ascertain whether a continent existed in the southern latitudes of the Pacific Ocean. (National Library of Australia)
On June 3, 1769, Cook, naturalist Joseph Banks, astronomer Charles Green and naturalist Daniel Solander recorded the transit of Venus from the island of Tahiti.
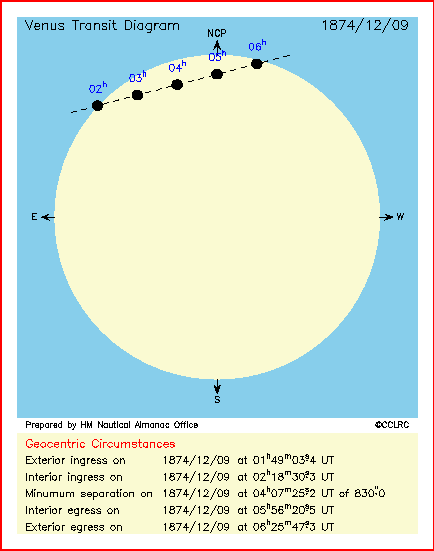
Then, “Early in 1869, one hundred years after British transit of Venus observations were made by James Cook and Charles Green from Tahiti George B. Airy, the seventh astronomer royal at Greenwich, wrote to the secretary of the Admiralty: ‘It appears from the calculations of Astronomers that there will occur, on 1874 December 8 and 1882 December 6, Transits of the planet Venus over the Sun’s Disk.’” (Chauvin)
“Eight American expeditions were fitted out in 1874, organized by the Transit of Venus Commission, with Simon Newcomb (1835-1909) as the official Secretary of the Commission. The US Congress appropriated funds totaling an astounding $177,000 for the expeditions.” (Harbster, LOC)
On September 9, 1874, fewer than seven months after the ascension to the throne of Hawai‘i King David Kalakaua, a ship from England, H.M.S. Scout, arrived in Honolulu carrying an expedition of seven astronomers.
“They came, as Captain Cook had come almost 100 years earlier, as the beneficiaries and instruments of a rich astronomical heritage that had found its visible embodiment in the Royal Observatory at Greenwich …”
“… and it was from Greenwich that Western astronomy had reached out to touch Hawai‘i in 1778, and was to do so again in 1874.”
“The mission of the 1874 expedition was to observe a rare transit of the planet Venus across the sun for the purpose of better determining the true value of the Astronomical Unit”. (Chauvin)
“King Kalakaua manifested a personal interest in the transit of Venus operations in his kingdom. And although he was absent from the islands when the much-awaited event occurred, he visited the transit of Venus observatory, as did other members of Honolulu’s society, both before and after ‘Transit Day.’” (Chauvin)
The King allowed the British Royal Society’s expedition a suitable piece of open land for their viewing area; it was not far from Honolulu’s waterfront in a district called Apua (mauka of today’s Waterfront Plaza.)
They built a wooden fence enclosure and soon a well-equipped nineteenth-century astronomical observatory took shape, including a transit instrument, a photoheliograph, a number of telescopes and several temporary structures including wooden observatories.
Subsequently, auxiliary stations – though not so elaborate as the main station in Honolulu – were established in two other island locations: one at Kailua-Kona and the other at Waimea, Kauai.
In addition, Hawai‘i was not the only site to observe the transit; under the British program, observations were also made in Egypt, Island of Rodriquez, Kerguelen Island and New Zealand. (Other countries also conducted Transit observations.)
On Dec. 8, 1874, the transit was observed by the British scientists; however, the observation at Kailua-Kona was marred by clouds. But the Honolulu and Waimea sites were considered perfect throughout the event, which lasted a little over half a day.
After the Transit of Venus observations, Kalākaua showed continued interest in astronomy, and in a letter to Captain RS Floyd on November 22, 1880, he expressed a desire to see an observatory established in Hawai‘i. He later visited Lick Observatory in San Jose.
An outcome of the Transit event in Hawai‘i was the ‘Transit of Venus lei’ … “Old residents may recall the white paper star lei that was in vogue here in the ’70s, commemorating the Transit of Venus of 1874.”
“They were appropriately called Hoku (star), and were made of stiff, white paper, forming many points, to convey the idea of scintillation. They were fashionable for some time, for hair or hat decoration, and were known to foreigners as Venus leis.” (Thrum HAA, 1922)
They came under other names, as well … “We have seen men, women, and children greatly engrossed in decorating their hats with this kind of lei. These are the names we have heard, “the hooulu lahui lei of Kalakaua,” “the Astronomer lei,” and “paper star lei.” (Ka Lahui Hawaii, Buke I, Helu 1, Aoao 1. Ianuari 1, 1875)
(International expeditions and observers soon refined this astronomical unit (an “astronomical unit” is the scientific term for a unit of measure equal to the average distance from Earth to the Sun) to 95 million miles by 1769, and then to 92.79 million miles by 1891.)
(During the twentieth century, the same radar technology that astronomers use to map the face of Mercury, or study the rings of Saturn, has yielded a precise value for the distance between the Sun and Earth of 92.9558203 million miles, with a margin of error of less than a few miles.) (LOC)