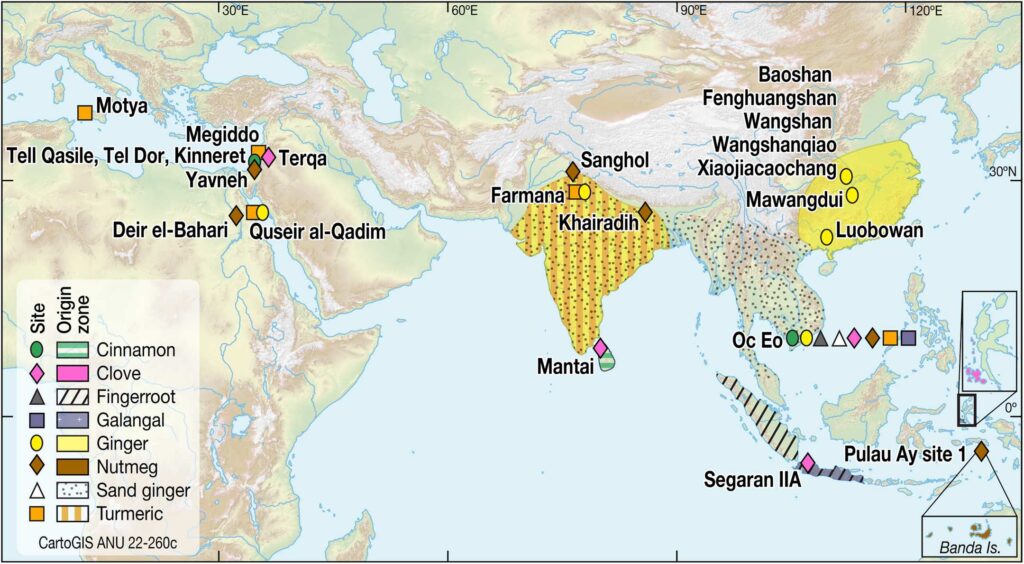
The word ‘spice’ is derived from the Latin ‘species’, or ‘special wares’, and refers to an item of special value, as opposed to ordinary articles of trade. Spices were highly valued because, as well as being used in cooking, many had ritual, religious or medical uses.
They were of high value because of their relative geographical scarcity. Spices could only be grown in the tropical East; South Asia served as a major source of spices – in the South of China, Indonesia, as well as in Southern India and Sri Lanka.
Among the most widespread were the spices cinnamon, pepper, clove, nutmeg, and mace. (Hancock) Some spices, such as cloves and nutmeg, grew nowhere else in the world.
The spice trade was conducted mostly by camel caravans over land routes (known as the Silk Roads). The Silk Roads were important routes connecting Asia with the Mediterranean world, including North Africa and Europe. (Deepanjana, UNESCO)
From as early as 2000 BC, spices, such as cinnamon from Sri Lanka and cassia from China, were exported along the Silk Road as far west as the Arabian Peninsula and the Iranian Plateau. Other goods were also exchanged/traded – cargoes from China included ivory, silk, porcelain, metals and gemstones. (Deepanjana, UNESCO)
Later, Spice Routes were established; these were the name given to the network of sea routes that linked the East with the West. The journey of the goods between all these links in the chain is called a trade route (the word ‘trade’ derives from a term meaning a track or course).
One of the major motivating factors in the European Age of Exploration was the search for direct access to the highly lucrative Eastern spice trade.
in 1513, a Spanish captain, Vasco Nuñez de Balboa, went into the interior of Darien (Panama). On September 24, 1513, Balboa sighted a new ocean. He called it the Mar del Sur, or ‘sea of the south’ (South Sea); later (1520), Ferdinand Magellan called it the Mare Pacificum, or Pacific Ocean.
The accounts of the first explorers revealed the potential for high-value commodity exchange, and voyages of exploration were soon followed by those of spice traders. (BOEM)
From 1500 AD onward, first Portugal, and then other European powers, attempted to control the spice trade, the ports which marketed spices, and eventually the territories which grew them. (Cartwright)
The Portuguese established trading posts in China at Macau in 1513, in Timor in 1515, and finally at Nagasaki, Japan in 1543. Within the next decades, Dutch competitors followed the Portuguese across the Indian Ocean and into Southeast Asia. (BOEM)
Then came the Spanish … on November 28 1520, Spaniard Fernao de Magalhais (Ferdinand Magellan) entered the eastern Pacific from the opposite direction, by way of the tip of South America, discovering the strait that now bears his name, and thereby opened up to Spain the possibility of an alternative route between Europe and the spices of the Orient.” (Lloyd)
Magellan crossed the ocean to the Philippines, which he named Las Islas Filipinas in honor of the Spanish king, Felipe. (Spate) The Spanish ultimately prevailed against other European competition in terms of Pacific trade. They did this through the founding of their outpost at Manila (Philippines) in 1571 and the establishment of regular transpacific Manila Galleon voyages.
Once a year, gold and silver were transported west from Acapulco to Manila in exchange spices (pepper, clove and cinnamon), porcelain, ivory, lacquer and elaborate fabrics (silk, velvet, satin), collected from both the Spice Islands (Moluccas, Indonesia) and the Asian Pacific coast.
The Pacific fur trade was pioneered by the Russians, working east from Kamchatka along the Aleutian Islands to the southern coast of Alaska. (ESDAW)
Originally, Russia exported raw furs, consisting in most cases of the pelts of martens, beavers, wolves, foxes, squirrels, and hares. Between the 16th and 18th centuries, Russians began to settle in Siberia, a region rich in many mammal fur species, such as Arctic fox, lynx, sable, sea otter and stoat (ermine).
it was the French and British who dominated Pacific exploration in the eighteenth century. Beginning in the mid-1700s, the rival nations began to send out scientific expeditions to explore and chart the islands of the Pacific.
British explorers included Samuel Wallis (1767–68) and Philip Carteret (1767–68). But by far the most wide-ranging and accomplished of the eighteenth-century explorers was the Englishman Captain James Cook, who made three separate voyages to the Pacific in 1768-71, 1772-75, and 1776-80. (Kjellgren, MetMuseum)
After Cook was killed in Hawai‘i, one of his officers – and later a Captain – George Vancouver continued to explore and chart the Northwest Coast. Commercial traders soon followed, exchanging copper, weapons, liquor, and varied goods for sea otter pelts. (Barbour)
Following Cook’s ‘discovery’ of the opportunities in the fur trade, the North American maritime fur trade became the earliest global economic enterprise. Cook’s ‘discovery’ resulted in the British and then the Americans participating in the trade.
Following the American Revolution, the new nation needed money and a vital surge in trade. In 1787, two ships (Columbia, captained by John Kendrick, and Lady Washington, captained by Robert Gray) left Boston on a mission around Cape Horn and into the Pacific Ocean. to establish new trade with China, settle an outpost on territory claimed by the Spanish, and find the legendary Northwest Passage.
Within ten years after Captain Cook’s 1778 contact with Hawai‘i, the islands became a favorite port of call in the trade with China. The fur traders and merchant ships crossing the Pacific needed to replenish food supplies and water.
Needing supplies in their journey, the traders soon realized they could economically barter for provisions in Hawai‘i; for instance, any type of iron, a common nail, chisel or knife, could fetch far more fresh fruit, meat, and water than a large sum of money would in other ports.
A triangular trade network emerged linking the Pacific Northwest coast, China and the Hawaiian Islands to Britain and the United States (especially New England). Practically every vessel that visited the North Pacific in the closing years of the 18th century stopped at Hawai‘i for refreshment and recreation.
As trade and commerce expanded across the Pacific, numerous countries were looking for faster passage and many looked to Nicaragua and Panama in Central America for possible dredging of a canal as a shorter, safer passage between the two Oceans.
Finally, in 1881, France started construction of a canal through the Panama isthmus. By 1899, after thousands of deaths (primarily due to yellow fever) and millions of dollars, they abandoned the project and sold their interest to the United States.
After Panamanian independence from Columbia in 1903, the US restarted construction of the canal in 1905. Finally, the first complete Panama Canal passage by a self-propelled, oceangoing vessel took place on January 7, 1914.
Later, when Navy Commander John Rodgers and his crew arrived in Hawaiʻi on September 10, 1925 on the first trans-Pacific air flight, they fueled the imaginations of Honolulu businessmen and government officials who dreamed of making Hawaiʻi the economic Crossroads of the Pacific, and saw commercial aviation as another road to that goal.
Two years later on March 21, 1927, Hawaii’s first airport was established in Honolulu and dedicated to Rodgers. 1959 brought two significant actions that shaped the present day make-up of Hawai‘i, (1) Statehood and (2) jet-liner service between the mainland US and Honolulu (Pan American Airways Boeing 707.)
Here is a link for more on Explorers and Traders: https://imagesofoldhawaii.com/wp-content/uploads/Explorers-and-Traders.pdf